Body Double finder explorer & primer designer
Body Double enzymes are (generally Type IIS) restriction endonucleases possessing separated recognition and cleavage sites. They may be used to generate an overhang which is identical to the overhang of a Type IIP restriction endonucleases (for example: EcorI or BamHI) on a PCR fragment.
The primer designer facilitates the selection of appropriate Body Double enzymes for a particular cloning task. For a detailed description read our related paper in PLOS ONE and consider citing it when using this method.
When should I use a Body Double enzyme?
Body Double enzymes may help you to bypass a few kind of problems arising in genetic engineering. Such as:
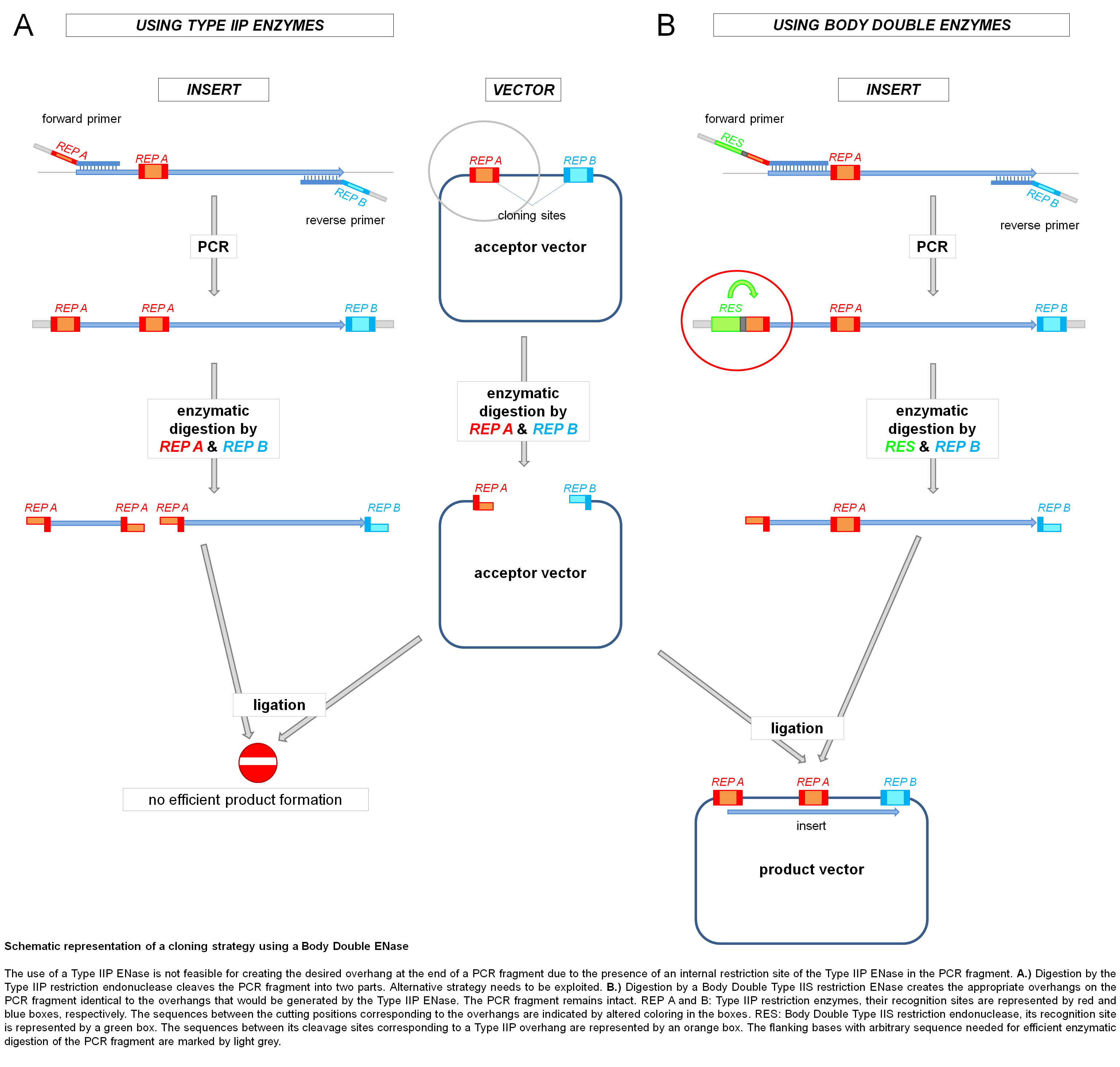
Genetic engineers' choices are frequently restricted to one or a few restriction endonucleases to clone a DNA fragment precisely to a specific position of a vector. The primary usefulness of employing restriction endonucleases as Body Doubles becomes evident when the problem of having a recognition site of the chosen restriction enzyme in the PCR fragment to be cloned arises. In such cases, the restriction enzyme that should be used for generating the overhang on the PCR fragment is simply substituted in the cloning strategy with a Body Double ENase that is able to generate the same overhang without cutting the PCR fragment at the pre-existing internal recognition site of the "original" Type IIP enzyme. Thus, digestion with the Body Double enzyme will generate overhangs on the PCR fragment that can be ligated to the acceptor vector opened with the original Type IIP restriction enzyme without the necessity of any modifications to the vector.
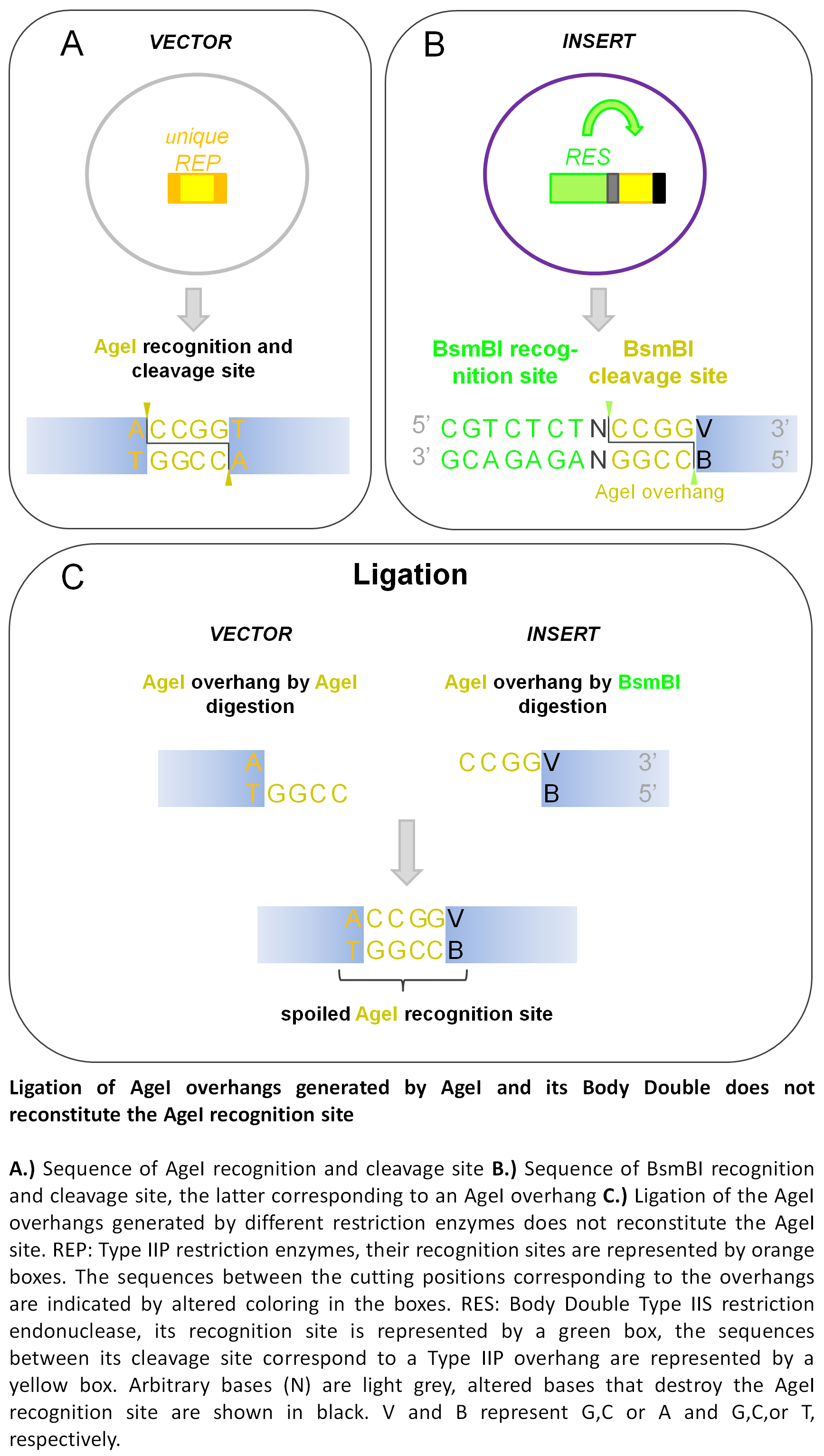
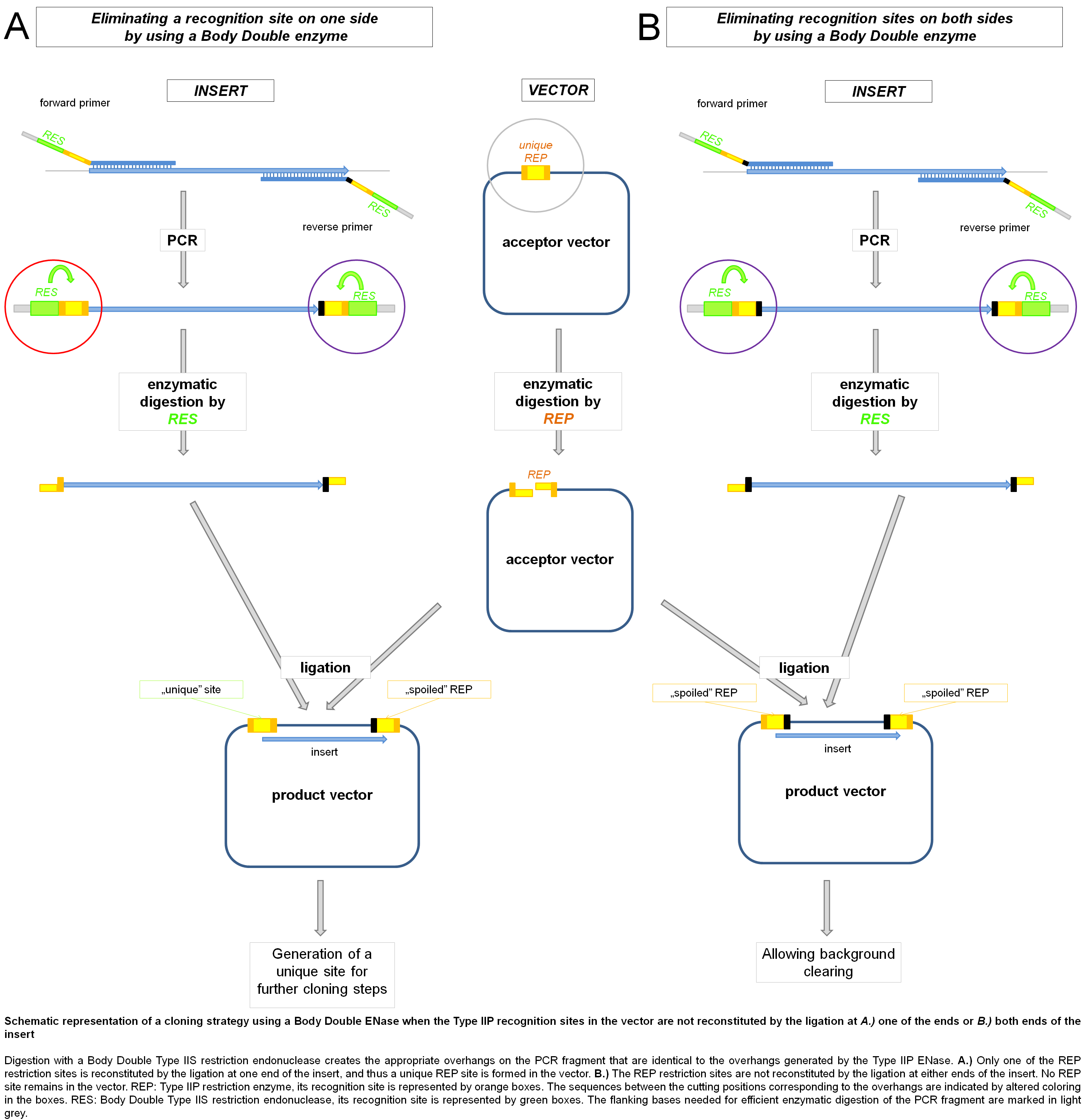
One such useful application of Body Double digestion is when the cloning site(s) in the vector needs to be eliminated from the product vector. The Type IIP ENases generally have a recognition site that also includes bases flanking the cleavage site. Thus, when primers are designed to determine the specificity of a Body Double enzyme, it is possible to either keep or destroy the Type IIP recognition site in the final vector product by varying the sequence of the flanking parts without changing the sequence of the overhang. The absence of the site used for cloning may be demanded (i) by downstream steps in a particular cloning strategy or (ii) for decreasing/clearing the background.
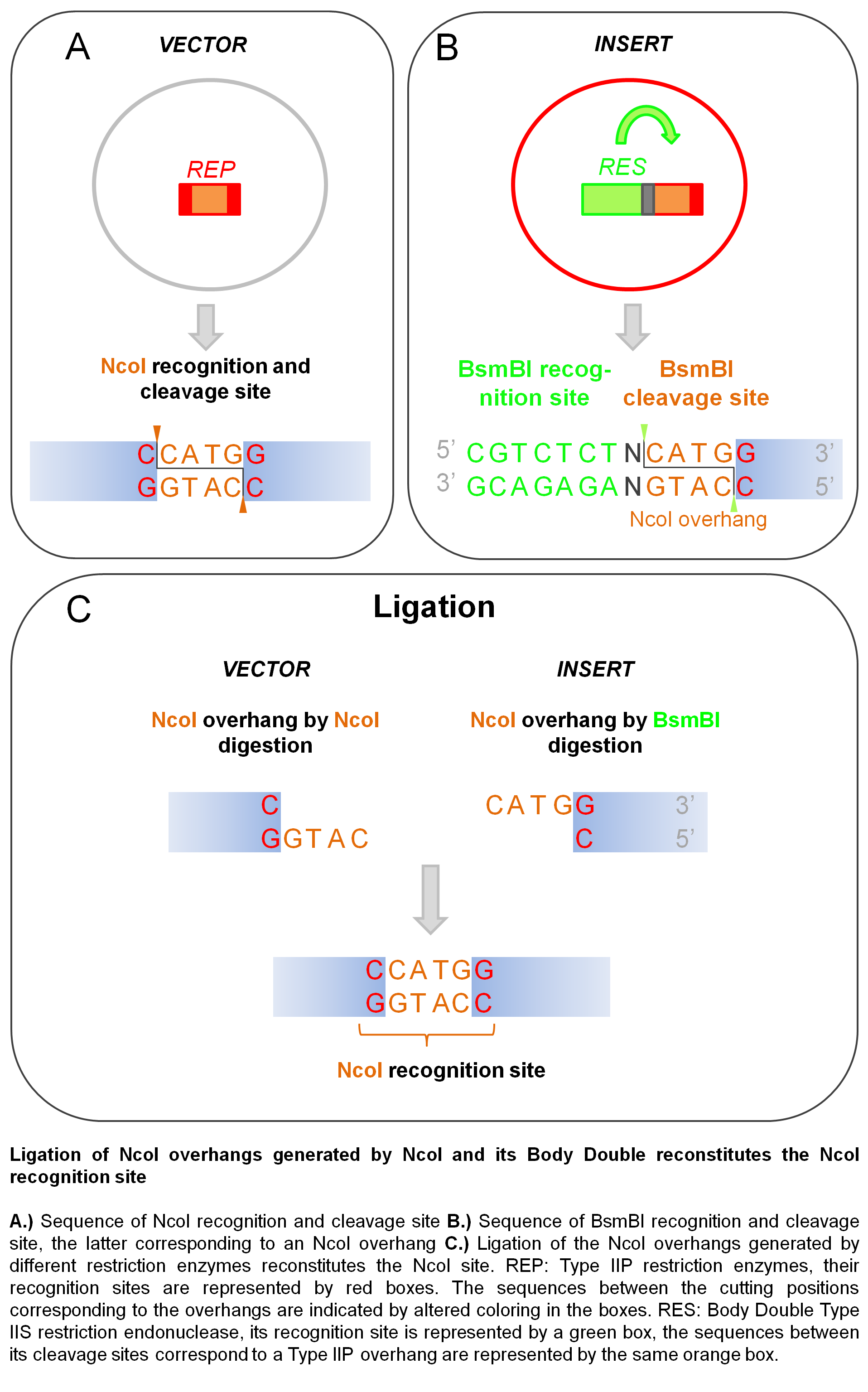
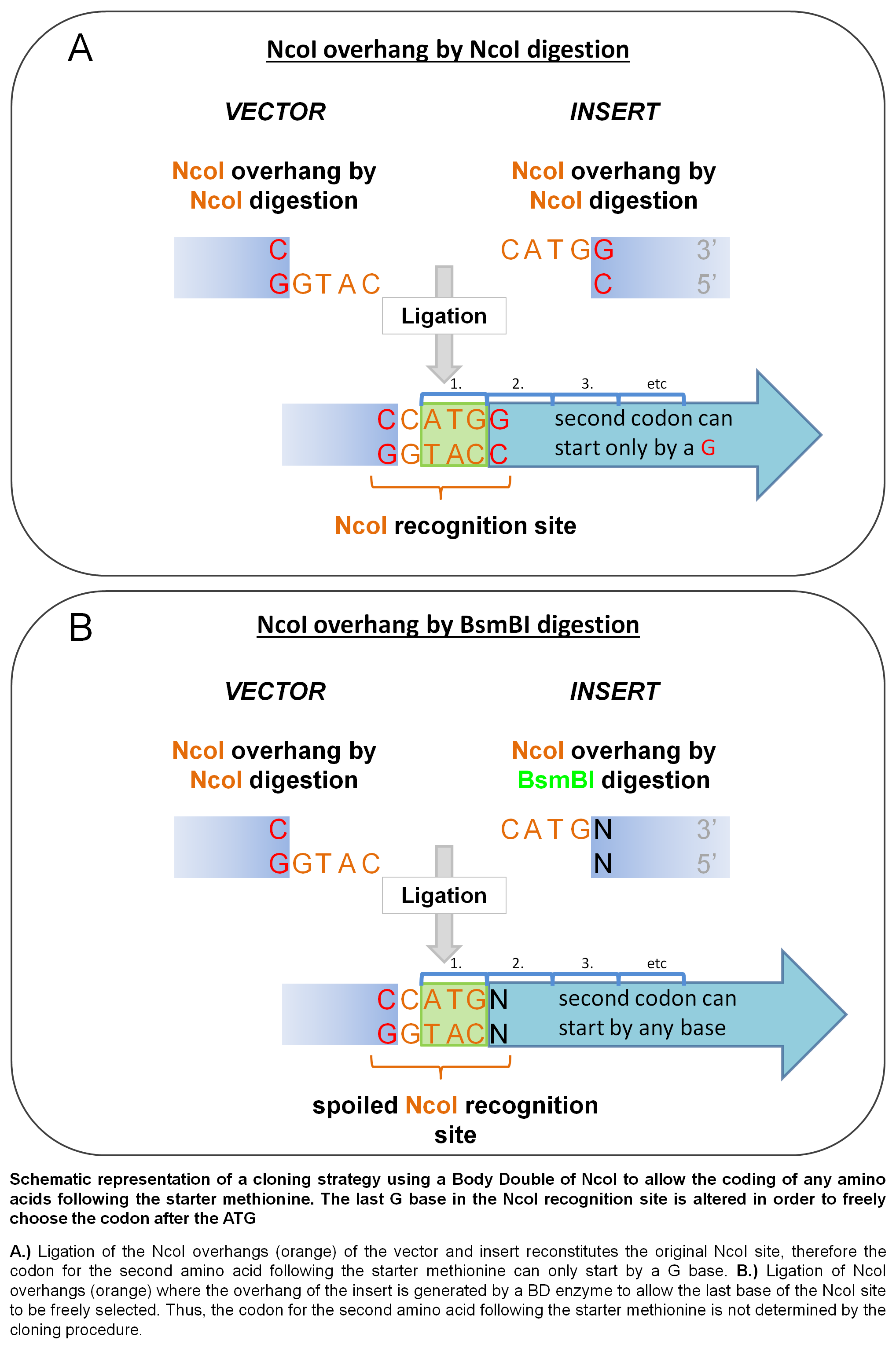
The elimination of the restriction site by using a Body Double may be particularly advantageous in the case of NcoI. NcoI and NdeI sites are frequently incorporated into the cloning site of expression vectors since they allow seamless incorporation of a fragment immediately following the first ATG triplet. Whereas linearization of the vector with NdeI allows any amino acid to be coded for by the codon following the first ATG codon, using NcoI (its recognition and cleavage site C’CATG_G) the possible amino acids that can be coded for in the second position is limited to codons starting with a G. When a BD of NcoI is used, the base in the position of the 3’ final G in the original NcoI site can be altered at will, allowing the second amino acid coded for be freely determined thus permitting the expression of polypeptides without introducing a mutation
An additional useful application of a Body Double enzyme is when the type of the protruding ends (with respect to the 3’ or 5’ ends and the length of the overhang) to be generated is identical at the two ends of a PCR fragment. Here a single Type IIS enzyme can be used as the Body Double of two different ENases at the same time. This strategy has the advantage that the digestion can be performed in a single step. Considering that the PCR fragments are frequently digested O/N and that the two selected restriction enzymes frequently have no compatible buffer for co-digestion, this strategy may provide reasonable benefits.
The following information needs to be provided:
- Select whether a forward or reverse primer is desired.
- The sequence of the PCR fragment to be cloned may be pasted in the box below.
- The name of the Type IIP enzyme or the choosen overhang type and sequence needs to be specified in the input box.
After providing the above, the designer will list the possible Body Double enzymes of the given Type IIP enzyme having no recognition site in the given sequence and design the primers that define the appropriate cleavage specificity.
