|
|
|
|
|
|
 | |
Microstructures created and driven by light |
Principal Investigator: Pál Ormos
This project is part of the EU-FP6 cooperation ATOM-3D
Previously we were succesful in fabricating light-driven machines held and rotated by laser
tweezers. Based on these experiences we managed to fabricate a light-driven micromotor out of
SU-8 photoresist which is attached to the surface of a microscope coverslip. The main goal was
to avoid the use of laser tweezers as the driving light source but use a light-guide instead.
Click the image below to see a computer animation of the concept.
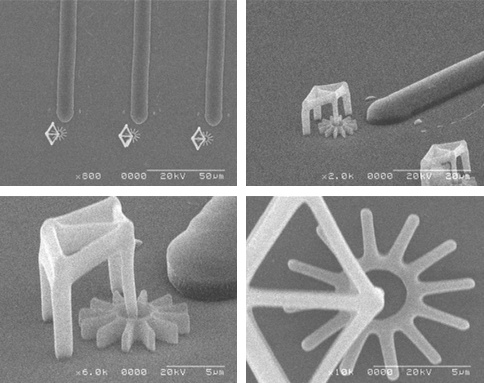
The light emerging from the end of the giude drives the motor. Furthermore, we managed to
integrate the lightguide also onto the same glass surface. The photopolymerised micromotor has
a 10µm diameter cog-wheel on an axis, similar to a water mill, which is held by an 8µm tall
supporting structure, and a light guide polymerised next to it. We positioned them such that the
emerging light interacts with the arms of the cogwheel, and makes it spin:
A video can be seen here. The speed of the cogwheel depends on the power of the driving laser.
The larger the power, the faster it spins. Until now we could achieve 2 rotations per second, but
with a relatively low laser power (~10mW).
Reference:
L. Kelemen, S. Valkai, and P. Ormos, Integrated optical motor, Appl. Opt. 45, 2777-2780 (2006).
Reference:
L. Kelemen, S. Valkai, and P. Ormos, Integrated optical motor, Appl. Opt. 45, 2777-2780 (2006).
| |


